ByJERUSALEM POST STAFF
Excessive alcohol consumption, poor diet, smoking, overuse of medications, and lack of exercise can silently damage the liver.
Five daily habits may cause serious harm to the liver and may later lead to death. The liver is one of the hardest-working organs in the human body. It performs essential functions for the body's balance, including detoxifying harmful substances, metabolizing nutrients, and producing substances fundamental for digestion.
Despite its remarkable resilience and capacity for regeneration, the liver is not indestructible. Excessive alcohol consumption is perhaps the most well-known cause of liver damage. When a person drinks alcohol, the liver works to break it down and eliminate it from the body, making it vulnerable to its effects. Excess alcohol overloads the liver's processing capabilities, causing the accumulation of toxic byproducts that damage liver cells and contribute to conditions such as alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Over time, the scarring can evolve into cirrhosis, where extensive hardening of the liver seriously affects its ability to function. Even moderate drinking can take a toll on the body if it continues for many years, especially if combined with other risk factors such as obesity or medication use. Experts recommend not consuming more than 14 units of alcohol per week and including alcohol-free days to give the liver time to regenerate.
Another habit that may cause silent damage to the liver is excessive use of painkillers. Many people turn to over-the-counter pain relievers like paracetamol for headaches, muscle aches, or fever. However, taking paracetamol in excess—even slightly exceeding the recommended dose—can be extremely dangerous for the liver. The liver breaks down paracetamol but produces a toxic byproduct called NAPQI in the process. In an overdose, glutathione stores are depleted, allowing NAPQI to accumulate and attack liver cells. This can result in acute liver failure, which can be fatal.
Smoking is also a risk factor for liver health. Cigarette smoke contains thousands of toxic chemicals that increase the liver's workload as it tries to filter and break them down. Over time, this can lead to oxidative stress, where unstable molecules (free radicals) damage liver cells, restrict blood flow, and contribute to scarring (cirrhosis). Harmful chemicals present in tobacco smoke, including nitrosamines, vinyl chloride, tar, and 4-aminobiphenyl, are known carcinogens. According to Al Arabiya, smoking exposes the liver to toxic substances that increase the risk of injuries and liver cancer.
Lack of exercise is another common habit that may cause silent damage to the liver. Physical inactivity contributes to weight gain, insulin resistance, and metabolic dysfunction—factors that can promote fat accumulation in the liver. Exercise can benefit the liver even without weight loss. A study found that just eight weeks of resistance training reduced liver fat by 13% and improved blood sugar control. Regular brisk walking for 30 minutes, five times a week, has been shown to reduce liver fat and improve insulin sensitivity.
Diet plays a role in liver health. Sugary foods and beverages, particularly those high in fructose, are risk factors for liver disease, leading to fat accumulation and potential liver damage. Excess fructose can lead to the development of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), previously known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). People who are overweight, especially those with abdominal obesity, are more likely to develop MASLD.
Oily, spicy foods, processed foods, and sugar-laden drinks are harmful to the liver. A diet rich in saturated fats, sugars, and ultra-processed foods favors the accumulation of fat in liver cells, increasing the risk of diseases such as hepatic steatosis. Adopting healthy habits, such as consuming alcohol in moderation, quitting smoking, maintaining a balanced diet, staying active, and staying hydrated, is the main strategy to keep the liver in good condition.
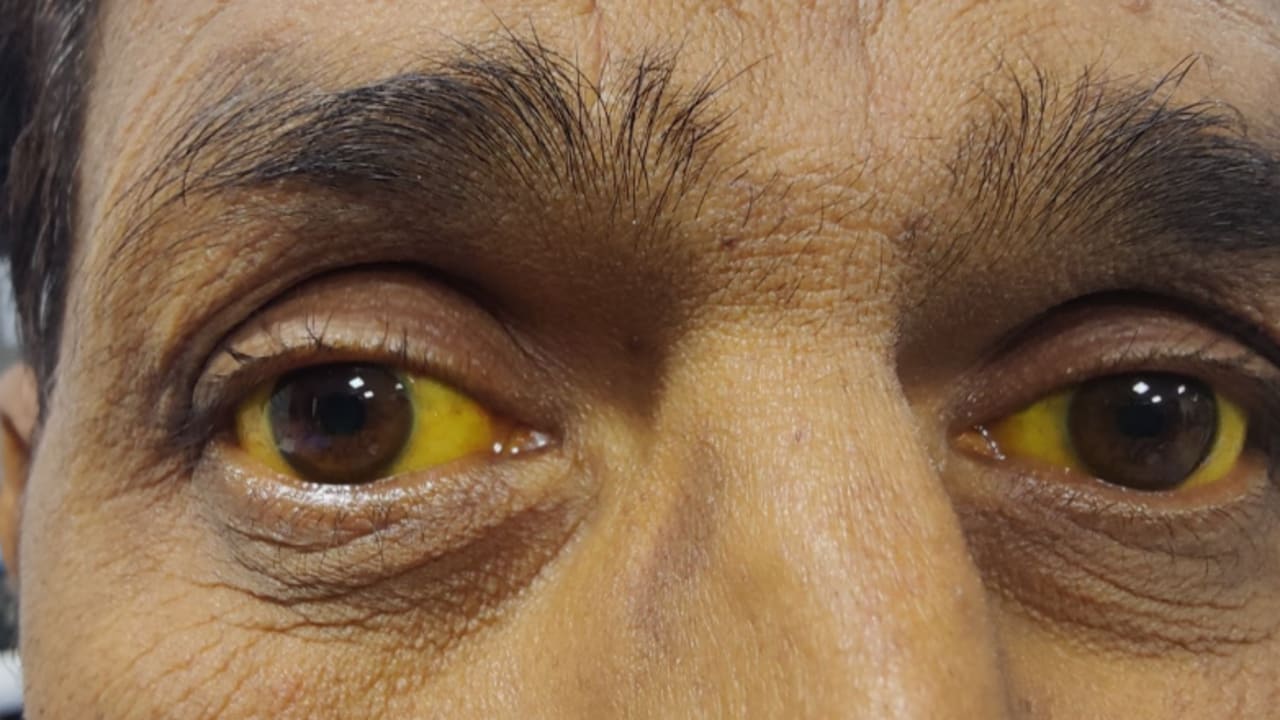
The development of liver diseases can occur silently, making it important to pay attention to habits that directly impact health, such as a sedentary lifestyle and smoking. In their early stages, liver diseases may cause only vague symptoms like persistent fatigue or nausea. As liver damage progresses, more evident signs may appear, such as jaundice, where the skin and the whites of the eyes become yellowed, and swelling in the legs and abdomen may also arise.
Ignoring liver care can result in serious complications, such as progression to cirrhosis, liver failure, and development of cancer. The earlier liver problems are detected, the greater the chances of successful treatment. If a person notices any symptoms that may suggest liver problems, such as persistent fatigue, nausea, or jaundice, they should not hesitate to consult their doctor.
To protect the liver, include fresh fruits, green vegetables, and a fiber-rich diet in your meals, while also limiting the intake of sweet drinks and processed foods. Staying hydrated is also important for liver health, and it is recommended to drink about eight glasses of water per day to assist the liver's natural detoxification processes. Recognizing the causes that can burden the liver's work early on is essential to prevent serious conditions.